
Heavy Menstrual Bleeding (Menorrhagia)
If your menstrual periods are so heavy that you dread your period and cannot maintain your usual activities, you may have excessive menstrual bleeding. Manorrhagia is the medical term for periods that are excessively heavy and last longer than normal.
Symptoms of Heavy Menstrual Bleeding
Symptoms of heavy bleeding during period may include needing to use double sanitary protection, having to change tampon or sanitary pad every hour for several consecutive hours, bleeding for longer than a week, and symptoms of anemia.
Causes of Heavy Menstrual Bleeding
Excessive menstrual bleeding is a common condition that occurs for many of reasons. Two of the most common causes are: a hormone imbalance and uterine growths.
Hormone Imbalances
Heavy menstrual bleeding may be caused by a variety of reasons, one being hormones which include estrogen and progesterone. Having too much or too little of certain hormones will cause an imbalance, which then causes heavy bleeding.
Causes of Hormonal Imbalances may Include:
- Certain medications
- Hormone changes in teens and in women nearing menopause
- Diabetes
- Thyroid disease
- Obesity
- Stress
- Strenuous exercise
- Eating disorders
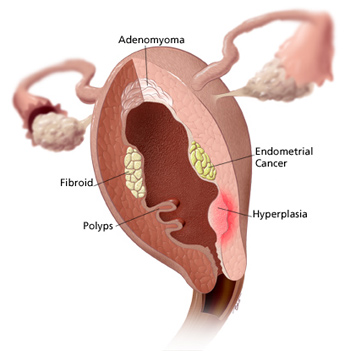
Types of Uterine Growths
- Uterine Fibroids – Benign or non-cancerous growths of the uterus
- Uterine Polyps – Growths that attach to the inner wall of the uterus and extend into the uterine cavity
- Adenomyosis – Occurs when endometrial tissue which normally lines the uterus grows into the muscular walls of the uterus
- Endometriosis– Disorder when the endometrium tissue grows outside your uterine cavity or uterus.
- Endometrial cancer – Starts in the inner lining of the uterus and the cells of the endometrium multiply without control
- Hyperplasia – An increase in the number of cells in a tissue or organ, and the lining of the uterus becomes too thick. It is also called endometrial hyperplasia.
PN 1002176 Rev A 04/2013
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Office on Women’s Health. FAQs. Available from:http://womenshealth.gov/
Serious complications may occur in any surgery, including da Vinci® Surgery, up to and including death. Examples of serious or life-threatening complications, which may require prolonged and/or unexpected hospitalization and/or reoperation, include but are not limited to, one or more of the following: injury to tissues/organs, bleeding, infection and internal scarring that can cause long-lasting dysfunction/pain. Risks of surgery also include the potential for equipment failure and/or human error. Individual surgical results may vary.
Risks specific to minimally invasive surgery, including da Vinci Surgery, include but are not limited to, one or more of the following: temporary pain/nerve injury associated with positioning; temporary pain/discomfort from the use of air or gas in the procedure; a longer operation and time under anesthesia and conversion to another surgical technique. If your doctor needs to convert the surgery to another surgical technique, this could result in a longer operative time, additional time under anesthesia, additional or larger incisions and/or increased complications.
Patients who are not candidates for non-robotic minimally invasive surgery are also not candidates for da VinciSurgery. Patients should talk to their doctor to decide if da Vinci Surgery is right for them. Patients and doctors should review all available information on non-surgical and surgical options in order to make an informed decision. For Important Safety Information, including surgical risks, indications, and considerations and contraindications for use, please also refer to www.davincisurgery.com/safety and www.intuitivesurgical.com/safety. Unless otherwise noted, all people depicted are models.


