
Endometriosis / Adenomyosis
Endometriosis is when tissue that is normally in the lining of the uterus grows outside the uterus. It may be painful and can be found on the ovaries, fallopian tubes, bowel and possibly other places in the pelvic cavity. Sometimes it can even grow outside the pelvis.
Growths or Lesions
This misplaced tissue develops into growth or lesions which respond to the menstrual cycle in the same way that the tissue of the uterine lining does, but the blood and tissue shed from endometrial growths has no way of leaving the body. The result, is internal bleeding, breakdown of the blood and tissue and inflammation. The inflammation can cause adhesions, which is scar tissue that can cause infertility.
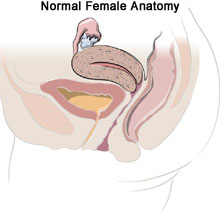
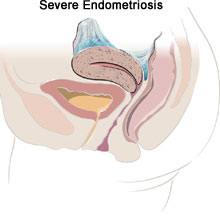
Endometriosis Causes
Endometriosis is a common gynecological condition especially for women of childbearing age. The cause of endometriosis is unknown but one theory suggests, during menstration some of the tissue backs up through the fallopian tubes into the abdomen, where it attaches and grows. Our doctors provide highly effective treatment to patients who are found to need it.
Common Symptoms of Endometriosis
With endometriosis, these symptoms may occur:
- Abnormal menstration
- Pain during intercourse
- Painful urination or bowel movements during menstrual period
- Fatigue
- Cramps and menstrual pain
- Pelvic pain
- Infertility – trouble getting pregnant (endometriosis)
Endometriosis Stages
The endometriosis/adenomyosis stages compared to the level of severity are as followes: stage 1- minimal, stage 2- mild, stage 3- moderate, and stage 4- severe. Staging of this condition depends on the number, size, and site of the implants. The stage depends on other factors such as the location, amount, depth, and size of the endometriosis implant. Pain does not determine the severity; some patients in a severe stage may not feel pain while some in stage 1 feel a lot of pain.
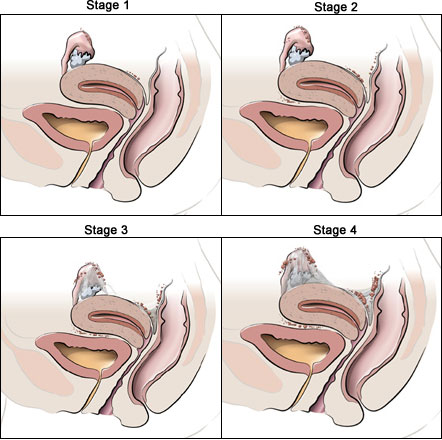
Learn More about Treatment & Surgical Options for Endometriosis
PN 1002240 Rev B 01/2014
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Office on Women’s Health. FAQs. Available from:http://womenshealth.gov/
Serious complications may occur in any surgery, including da Vinci® Surgery, up to and including death. Examples of serious or life-threatening complications, which may require prolonged and/or unexpected hospitalization and/or reoperation, include but are not limited to, one or more of the following: injury to tissues/organs, bleeding, infection and internal scarring that can cause long-lasting dysfunction/pain. Risks of surgery also include the potential for equipment failure and/or human error. Individual surgical results may vary.
Risks specific to minimally invasive surgery, including da Vinci Surgery, include but are not limited to, one or more of the following: temporary pain/nerve injury associated with positioning; temporary pain/discomfort from the use of air or gas in the procedure; a longer operation and time under anesthesia and conversion to another surgical technique. If your doctor needs to convert the surgery to another surgical technique, this could result in a longer operative time, additional time under anesthesia, additional or larger incisions and/or increased complications.
Patients who are not candidates for non-robotic minimally invasive surgery are also not candidates for da VinciSurgery. Patients should talk to their doctor to decide if da Vinci Surgery is right for them. Patients and doctors should review all available information on non-surgical and surgical options in order to make an informed decision. For Important Safety Information, including surgical risks, indications, and considerations and contraindications for use, please also refer to www.davincisurgery.com/safety and www.intuitivesurgical.com/safety. Unless otherwise noted, all people depicted are models.


